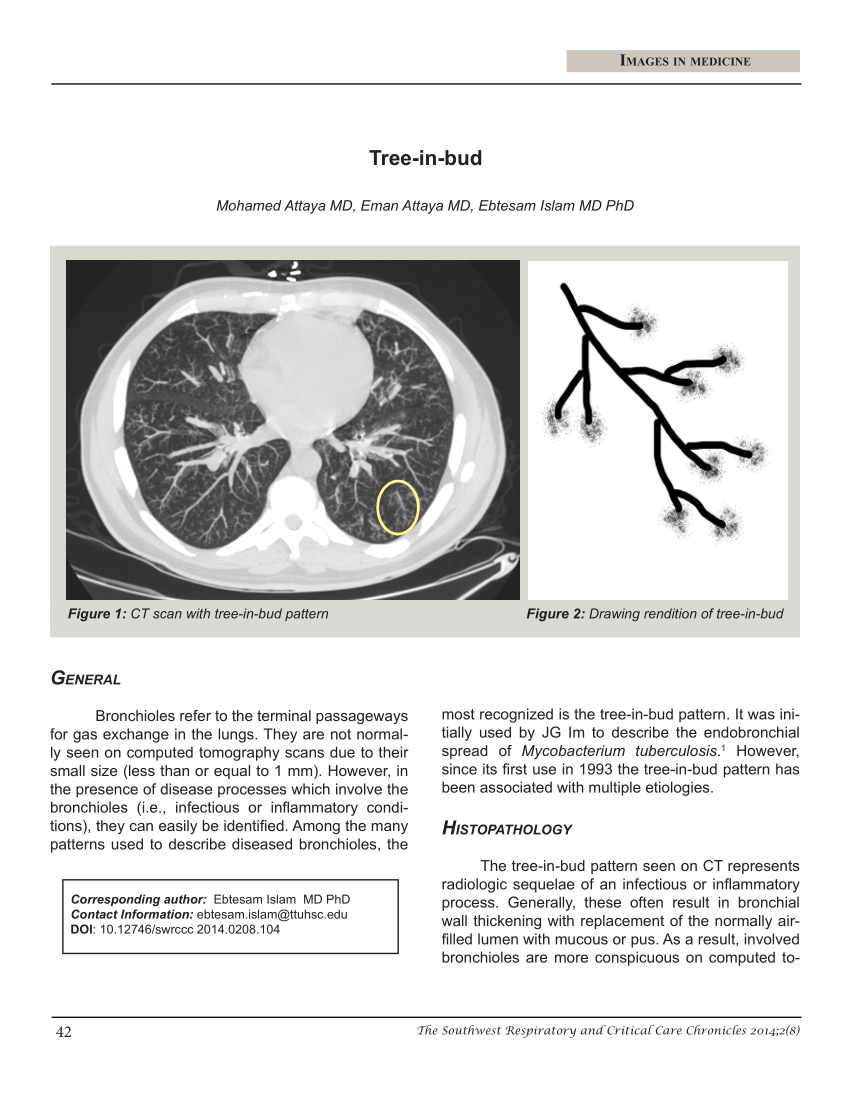
tree in bud opacities causes
The tree-in-bud sign can be commonly caused by respiratory infections including that of mycobacterial bacterial and viral causes. While the tree-in-bud appearance usually represents an endobronchial spread of infection given the proximity of small pulmonary arteries and small airways sharing branching morphology in the bronchovascular bundle a rarer cause of the tree-in-bud sign is infiltration of the small pulmonary arteriesarterioles or.

Computed Tomography Of The Chest Showed Nodular Opacities With Tree In Download Scientific Diagram
In infants and young children the tree-in-bud pattern is most commonly caused by bronchial wall thickening and dilatation related to respiratory syncytial virus.

. 1 2 3 4 reported causes include infections aspiration and a variety of inflammatory conditions. The classic cause of the tree-in-bud pattern is postprimary tuberculosis Fig. 78 indicating the absence.
Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. The classic cause of the tree-in-bud pattern is postprimary tuberculosis Fig. Where there is small airways disease and tree in bud is present this can be termed an exudative bronchiolitis.
Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses four of 166 3 or multiple organisms six of 166 4 were most common. Tib opacities are also associated with bronchiectasis and small airways obliteration resulting in mosaic air trapping. 3A 3B a condition that develops in approximately 5 of patients with primary infection and is frequently associated with malnutrition and immune suppression.
Found that the tree-in-bud pattern was seen in 256 of the CT scans in patients with bronchiectasis. What causes tree in bud opacities. The pattern of the tree correlates to an intralobular inflammatory bronchiole and the bud correlates to inflammatory filling in alveolar ducts.
We here describe an unusual cause of TIB during the COVID-19 pandemic. Bronchiectasis which may be of any cause can produce the tree-in-bud pattern. Respiratory infections 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65 of 166 39 bacteria 44 of 166 27 viruses four of 166 3 or multiple organisms six of 166 4 were most common.
Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. The purpose of this study was to determine the relative frequency of. Are tree-in-bud nodules cancerous.
Infective bronchiolitis bacterial pneumonia eg. Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. In infants and young children the tree-in-bud pattern is most commonly caused by bronchial wall thickening and dilatation related to respiratory syncytial virus.
Diffuse panbronchiolitis is an exudative bronchiolitis. Miller WT Jr Panosian JS. Causes and imaging patterns of tree-in-bud opacities.
However to our knowledge the relative frequencies of the causes have not been evaluated. What is a tree-in-bud opacity. Staphylococcus aureus Haemophilus influenzae Mycobact erium tuberculosis Mycobacterium.
The purpose of this study was to. The causes of TIB opacities. Another important entity that can produce the tree-in-bud pattern is bronchioalveolar carcinoma BAC.
Causes for TIB opacities were established in 166 of 406 409 cases. What causes tree-in-bud opacities. Tree in bud opacification refers to a sign on chest CT where small centrilobular nodules and.
Although initially described in 1993 as a thin-section chest CT finding in active tuberculosis TIB opacities are by no means restricted to a specific. As you can see the possible causes of a tree in bud appearance are legion. The main causes of tree-inbud findings in the general population are reported to be acute or chronic infections mainly from nontuberculous mycobacteria and.
1-4Reported causes include infections aspiration and a variety of infl ammatory conditions. Jennifer hong ba francisca zuazo md hanyuan shi md 1 1 tulane university la new orleans. In the hospital MTB cannot be missed.
The differential diagnosis of tree-in-bud nodules includes infection and aspiration the two most common causes as well as congenital airway diseases allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis follicular bronchiolitis panbronchiolitis intravenous injection of foreign material and intravascular tumor emboli. A young male patient who had a history of fever cough and respiratory distress presented in the emergency department. Respiratory infec-tions 119 of 166 72 with mycobacteria 65.
This is the classic appearance of the tree in bud pattern seen on chest ct. Tree-in-bud TIB opacities are a common imaging finding on thoracic CT scan. Tree in bud opacities treatment.
Viral pneumonia fungal pneumonia eg. Aspiration was the cause in 42 of 166 25. Staphylococcus aureus Haemophilus influenzae Mycobact erium.
Patterns of disease associated with TIB opacities were evalu ated. As you can see the possible causes of a tree in bud appearance are legion. Tree-in-bud TIB appearance in computed tomography CT chest is most commonly a manifestation of infection.
TIB opacities are most often a manifestation of infections or aspiration and patterns of disease can provide clues to the most likely diagnosis. BACKGROUND Multiple causes for tree-in-bud TIB opacities have been reported. 6 March 2014.

Pdf Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Semantic Scholar

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Tree In Bud Pattern Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
View Of Tree In Bud The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest

References In Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Chest
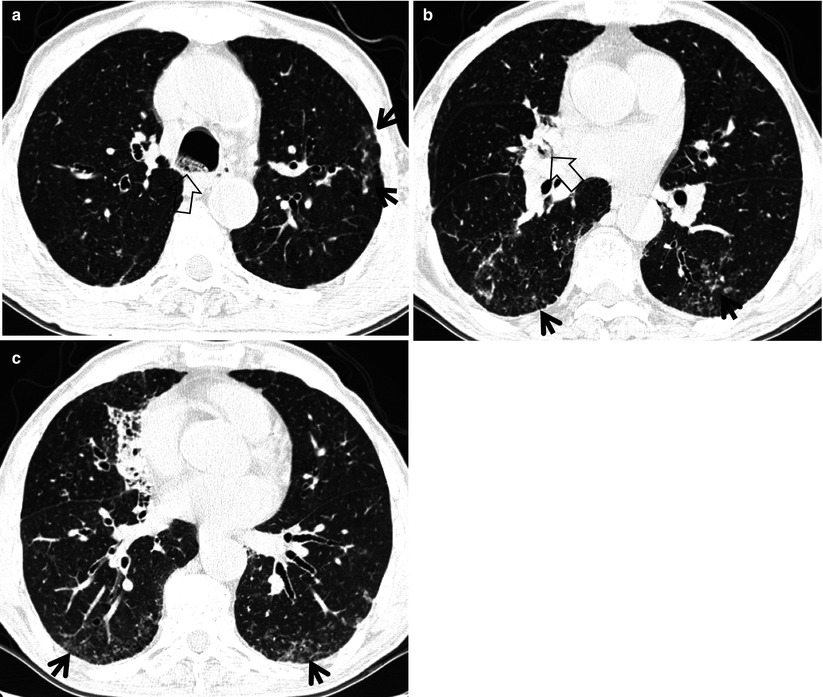
Tree In Bud Sign Radiology Key

Pdf Tree In Bud Semantic Scholar
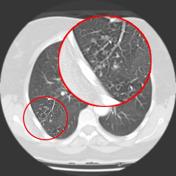
Tree In Bud Sign Lung Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Pdf Causes And Imaging Patterns Of Tree In Bud Opacities Semantic Scholar